Spectral Method PDE
The Poisson equation is given by:
$$\Delta u=f\:\:\:\in\Omega\:\:\: and \:\:\:u(z)=0 \:\:\:\forall\: z\in\partial\Omega$$
Kronecker product of two matrix \(A\) and \(B\) is given by:
$$A\otimes B=\begin{pmatrix}
a_{11}B&...&a_{1n}B\\
\vdots&\vdots&\vdots\\
a_{m1}B&...&a_{mn}B\\
\end{pmatrix}$$
In two dimensions the spectral operator can be constructed with the Kronecker product as following:
$$\Delta=I_y\otimes D_x+D_y\otimes I_x$$
The function \(f\) can be written in:
$$f=f(y)\otimes f(x)$$
This is equivalent to write the two dimensional object as one dimensional in the following way:
$$f_{j,i}\Rightarrow f_{i+N_x j}$$
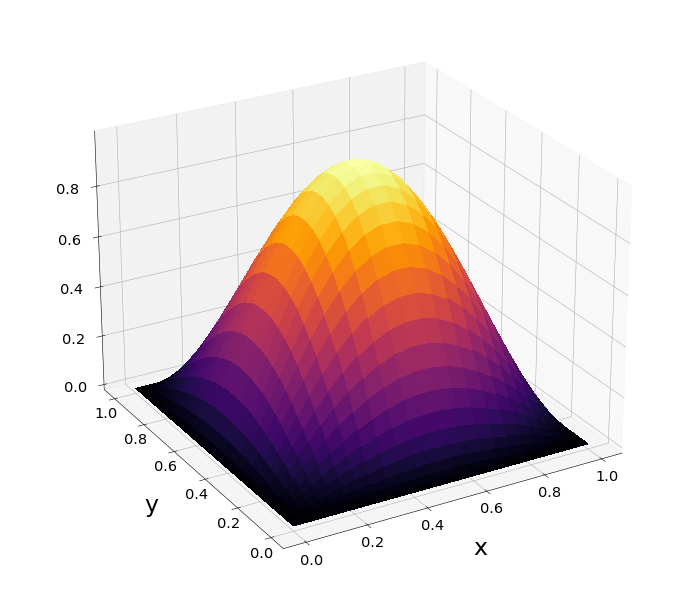
Figure 1: \(\Omega=[0,1]\times[0,1]\) and \(f=2\pi^2\sin{(\pi x)}\sin{(\pi y)}\)
"""The code below was written by @author: https://github.com/DianaNtz and
solves the Poisson equation via spectral methods. """
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
#create grid
def Cheb_grid_and_D(xmin,xmax,Nx):
x=np.zeros(Nx)
cx=(xmax-xmin)/2
dx=(xmax+xmin)/2
for j in range(0,Nx):
x[j]=-np.cos(j*np.pi/(Nx-1))*cx+dx
Dx=np.zeros((Nx,Nx))
Dx[0][0]=-(2*(Nx-1)**2+1)/6
Dx[Nx-1][Nx-1]=(2*(Nx-1)**2+1)/6
for i in range(0,Nx):
if(i==0 or i==Nx-1):
ci=2
else:
ci=1
for j in range(0,Nx):
if(j==0 or j==Nx-1):
cj=2
else:
cj=1
if(i==j and i!=0 and i!=Nx-1):
Dx[i][i]=-((x[i]-dx)/cx)/(1-((x[i]-dx)/cx)**2)*0.5
if(i!=j):
Dx[i][j]=ci/cj*(-1)**(i+j)/(x[i]/cx-x[j]/cx)
Dx=Dx/cx
return x,Dx,np.dot(Dx,Dx)
#Initial values
Nx=30
Ny=40
xmin=0
xmax=1.0
ymax=1.0
ymin=0.0
y,Dy,D2y=Cheb_grid_and_D(ymin,ymax,Ny)
x,Dx,D2x=Cheb_grid_and_D(xmin,xmax,Nx)
d2x=np.kron(np.identity((Ny)),D2x)
d2y=np.kron(D2y,np.identity((Nx)))
f=np.zeros(Ny*Nx)
for j in range(0,Ny):
for i in range(0,Nx):
f[i+j*Nx]=-2*np.pi**2*np.sin(np.pi*y[j])*np.sin(np.pi*x[i])
#create Laplace operator
L=d2y+d2x
#setting boundaries
bound=np.kron(np.identity((Ny)),np.identity((Nx)))
b=f
for j in range(0,Ny):
for i in range(0,Nx):
if(i==0):
b[i+j*Nx]=0
if(i==Nx-1):
b[i+j*Nx]=0
if(j==Ny-1):
b[i+j*Nx]=0
if(j==0):
b[i+j*Nx]=0
for k in range(0,Ny*Nx):
if(k%Nx==0):
#z bei 0
L[k]=bound[k]
if(k < Nx ):
L[k]=bound[k]
#rho bei 0
if(k%Nx==Nx-1):
L[k]=bound[k]
#z bei Nz
if(k>=Ny*Nx-Nx):
L[k]=bound[k]
#rho bei Nrho
#solve linear system
solution=np.linalg.solve(L,b)
print(np.linalg.matrix_rank(L,tol=0.000000000000001))
print(Ny*Nx)
so=solution.reshape(Ny,Nx)
#plotting results
xx,yy= np.meshgrid(x, y)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(14,12))
axx = plt.axes(projection='3d')
axx.plot_surface(xx, yy, so,cmap=cm.inferno,antialiased=False)
axx.view_init(azim=240,elev=25)
axx.set_xlabel('x', labelpad=30,fontsize=34)
axx.set_ylabel("y",labelpad=30,fontsize=34)
axx.zaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=21,pad=18)
axx.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=21)
axx.xaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=21)
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1, bottom=0, top=1)
filename ="PDE.png"
plt.savefig(filename,dpi=50)
plt.show()